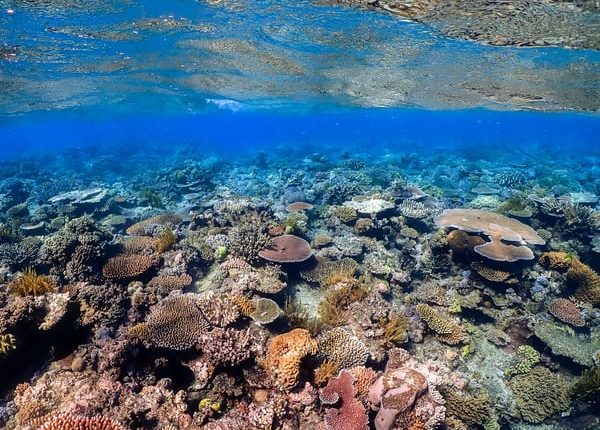
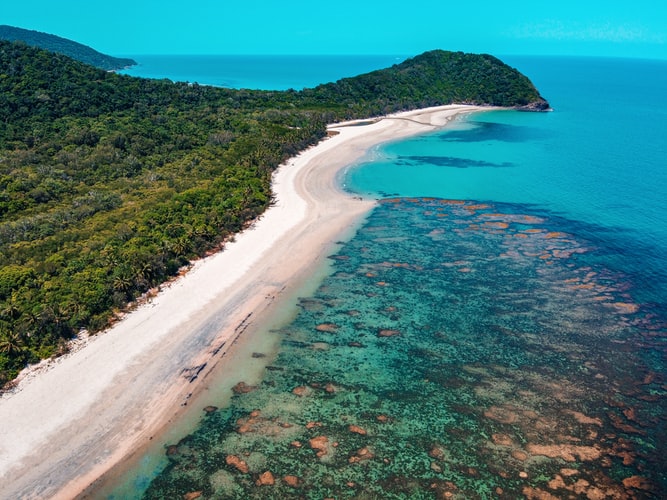
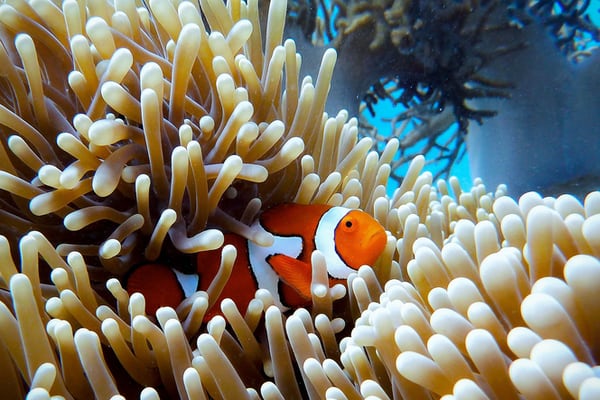
One of the natural world’s greatest wonders, the Great Barrier Reef off the eastern coast of Australia, has lost over half of its corals in the past 25 years a new study has announced.
The Great Barrier Reef stretches for more than 2,300km along the Queensland coast, and in 1981, was designated a World Heritage Site for its “enormous scientific and intrinsic importance” to the planet.

Warnings about the reef’s demise have been consistently ignored at both the national and local level levels for decades, with a clamor for the tourist dollar taking precedence along much of the Queensland Coast.
Significant in the finding is the fact that the decline has affected all forms of coral found on the reef, and unlike previous examples of coral loss around the world has not been linked solely to certain types.
Branching and table-shaped corals were the worst affected, however – both serving as the base habitats for large numbers of fish species and other sea life.
The study, released in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B (a biological research journal) also revealed that the worst periods of coral loss came about from ‘mass bleaching’ across 2016 and 2017, and then again early in 2020.
Dr. Andy Dietzel, the study’s lead author said “(A) vibrant coral population has millions of small, baby corals, as well as many large ones,” adding “Our results show the ability of the Great Barrier Reef to recover – its resilience – is compromised compared to the past, because there are fewer babies, and fewer large breeding adults.”
Another of the study’s authors, a Professor Hughes said of the bleaching and overall decline: “We used to think the Great Barrier Reef is protected by its sheer size – but our results show that even the world’s largest and relatively well-protected reef system is increasingly compromised and in decline.”